Blockchain technology has also given rise to a new form of organisation: a DAO or Decentralized Autonomous Organization. Spurred by their capabilities, DAOs are increasingly becoming popular in the digital world. But first, what is a DAO? What is the meaning of the word DAO and why do we need them in the crypto space?
What is a DAO?
The literal meaning of a DAO is ‘Decentralized Autonomous Organization’. But what is a DAO really? Essentially, a DAO is an organization run by a group of people with no typical company hierarchy. Then, they establish their own rules, and make decisions based on votes.
Essentially, a DAO works like a corporation with no executive board—a company that can seamlessly function autonomously and without leadership. Its main role is to bring together a community of people with similar interests to work towards a common goal.
The History Of Decentralized Autonomous Organizations in Crypto
Bitcoin is widely considered the first-ever DAO. However, another famous origin of a Decentralized Autonomous Organization dates back to 2016 when few members of the Ethereum community set up what they called ‘The DAO’ on the Ethereum blockchain. The developers founded it to function as a venture capital fund sans any board of directors. Essentially, anyone could pitch their idea to the community to potentially secure funding from The DAO. It launched in late April 2016 after its ICO (initial coin offering) raised close to $150 million—the largest crowdfunding effort at the time.

However, due to some vulnerabilities in its code, hackers managed to steal $50 million worth of ETH from the DAO in June 2016. The incident—one of the biggest crypto hacks in history—eventually led to the fall of the organization. Nonetheless, following the mass adoption of DeFi, more and more DAOs are now popping up worldwide.
How Does A DAO Work?
Decentralized Autonomous Organizations operate on a set of rules and regulations established through smart contracts on a blockchain. Firstly, smart contracts are immutable, open protocols programmed to execute automatically if and when certain pre-established conditions are met. These are publicly available and verifiable, meaning any member can easily view the contract, all decisions, and financial transactions of the DAO.
Thus, through smart contracts, these organizations are fully transparent. Additionally, as DAOs are decentralized, no central authority can override or make changes to the smart contract. Any change only comes with the community’s majority vote.
Typically, a person will need to own a token to participate in a DAO. Then, token ownership also comes with governance/voting rights. Basically, they can influence decisions in the organization by creating and voting for proposals. Proposals can include decisions about the organisation’s future, how to utilise funds, and much more. The more tokens a person has, the higher will be their voting power. Furthermore, for a proposal to be passed, it must receive votes from the majority of token holders as well as meet the DAO’s rules and regulations.
In certain cases, like with ConstitutionDAO, people don’t need to invest in the organization to become members. To illustrate, this particular decentralized organisation allowed crypto enthusiasts to buy a first-edition copy of the US Constitution. It went on to raise $40 million in funds but to no avail.
Now that we know the meaning of a DAO, let’s see how it relates to NFTs and Crypto.
So, what do DAOs have to do with NFTs?
The short answer? A lot.
From collective ownership of NFTs to governance and more, Decentralized Autonomous Organizations bring a lot to the NFT world.
Collective ownership
One way Decentralized Autonomous Organizations help the NFT industry is in collective ownership of an asset. Usually, investing in NFTs, especially blue-chip projects, requires significant capital. Of course, not everyone can afford this. Thus, some DAOs were established to allow a group of people to collectively own a high-value NFT without shelling out thousands of dollars.
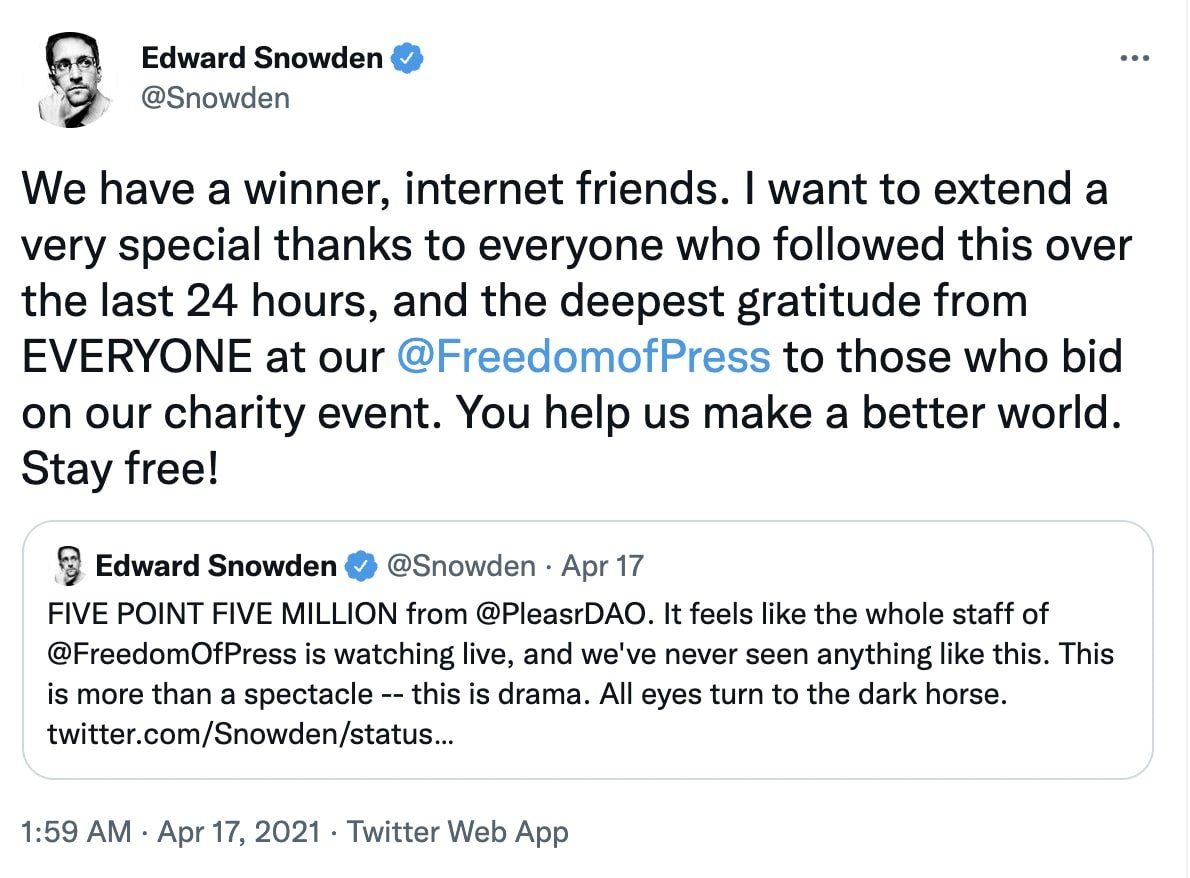
Take PleasrDAO for example. It is a collective of “DeFi leaders, early NFT collectors, and digital artists” that collects funds for highly valuable NFTs. According to its website, the organization collects digital art that “represents and funds important ideas, movements, and causes”. For all the NFTs it buys, PleasrDAO members collectively share the cost and ownership of the assets. The members had originally set up the organization to buy a Uniswap V3 NFT. However, it has now purchased NFTs like Edward Snowden’s NFT “Stay Free”—the only one in existence. PleasrDAO bought it for 2,224 ETH or around $5.4 million at the time!
Community governance
Another key area where Decentralized Autonomous Organizations help NFTs is community governance. Firstly, DAOs are a great means for fans and creators of an NFT project to come together and decide its future. Several NFT projects have already established their own Decentralized Autonomous Organizations.
For example, top collectible, Gutter Cat Gang has the Gutter Cat Gang DAO. The organization, as per its website, aims to take the Gang “beyond that of your standard NFT community or club”. Here, those who own Gutter Cat NFTs get to vote on certain decisions such as community project initiatives. While the smart contract is currently “more controlled”, the project claims it will eventually become 100% decentralized. Furthermore, the Gutter Cat Gang DAO also hosted a Las Vegas party exclusively for the NFT holders!
In some cases, the community creates Decentralized Autonomous Organizations and not the project itself. A typical example is MeebitsDAO set up by community members of Larva Labs’ Meebits NFT project. Via the DAO, the community aims to build a metaverse for the avatars. For this, the organization plans to buy virtual land in various metaverses.
NFT creator collectives
A strong community backing is essential for an NFT project’s success. For popular artists and celebrities that already have a following, community building is a walk in the park. However, that’s not the case for emerging artists. This is where NFT creator collectives governed by Decentralized Autonomous Organizations come into the picture. Essentially, these are a collective of NFT creators that helps to raise funds, marketing, community building, and more.

Typically, artists have to sell their NFT to the DAO in exchange for the DAO’s tokens. The NFTs, in a way, work as collateral for the issued tokens and give the token value. Additionally, token holders get voting rights in the organization. An example is WHALE, a social token backed by The Vault—the platform’s NFT art collection. A DAO governs the Vault, whose members hold the WHALE tokens and contribute to the project’s growth.
What are the different types of DAOs?
Let’s take a look at the different types of DAOs.
1. Social DAO
As the name implies, Social DAOs are collaborative platforms for social networking in the crypto space. Often, members of these decentralised organisations have a common interest such as arts and culture. A popular example of a Social DAO is Friends with Benefits (FWB), which focuses on unifying artists and cultural creators who share similar values. The organisation describes itself as a “collective of unique individuals pushing for a bright future”. FWB also has its own social token, $FWB.
2. Investment DAO
In Investment DAOs (or Venture DAOs), a group of people come together to raise money for various DeFi activities. These decentralised organisations are transparent and democratise investing, thereby attracting younger generations who want to make some money. Mostly, these DAOs are inclusive and open to pretty much anyone. Together, the DAO members makes investments decisions—such as which artwork or project to invest in. Honestly, the limit is endless—the DAO could even invest in an entire sports team. Some examples include the Meta Cartel DAO, which invests in Ethereum projects, and The Krause House, a Decentralized Autonomous Organization dedicated to NBA fans.

3. Collector DAO
Collector DAOs focus on collectively buying NFTs, just like the Pleasr DAO mentioned earlier. Essentially, Collector DAOs enable members to fractionally own blue-chip projects or other highly-priced digital assets in the space. This is how these organisations work—memebers collectively pool funds together to invest in an artwork/collectible of their choice. Other examples of Collector DAO includes Flamingo and Constitution DAO.
4. Grant DAO
Grant DAOs represent one of the primary uses of DAOs—to collects funds in the ‘Grant Pool’ and allocate them based on a community vote. Mostly, these DAOs focus on funding interesting DeFi projects. In a way, these organisations function as decentralised Venture Capitalists—the organisations can submit applications and the DAOs pick ones they like and provide funds. Examples include Moloch DAO, Aave Protocol, and Audius Grants.

5. Protocol DAO
In Protocol DAOs, certain smart contract protocols are used to provide decentralised financial services. Typically, they will have tokens that function as a voting metric to bring forth any changes in the protocol and make financial changes. In short, these decentralised organizations enable anyone to become part of the the global financial system. Some Protocol DAOs are MakerDao, Uniswap, SushiSwap, and Olympus.
6. Entertainment DAOs
Entertainment DAOs allow members to put their thinking caps on and let their creativity flow. Meaning, members with shared values come together through these types of DAO to bring a creative project to life. Take for example Fluf World. It allows its members to customize their 3D NFT Flufs and even license them out. Apparently, BAYC also plans to set up its own Entertainment DAO.
Some popular NFT DAOs
Wondering what are some of the most popular NFT DAOs? Here are our picks:
APE DAO
APE DAO was started by Bored Apes collector Kylo.eth. They fractionalized 49 BAYC NFTs and a female CryptoPunk into 1,000,000 APED tokens to launch the decentralised organizations in June this year. Meaning, as part of their DAO, anyone could own parts of these highly sought-after NFTs. The Decentralized Autonomous Organization was a great success with the tokens selling out in just four days! Soon after, the members donated more NFTs, including CyberKongz, Avastar, Punk’s Comic, and more. Furthermore, the community governs the DAO through $APED shards.

YGG DAO
As opposed to NFT art and collectibles, YGG DAO focuses on in-game assets from blockchain and NFT games. Currently, Yield Guild’s three co-founders manage all the assets. Furthermore, YGG issues the ‘YGG token’ for members. Accordingly, Token holders can vote on “decisions related to the guild’s business and governance” and participate in various activities.
SharkDAO
SharkDAO brings together a group of strangers to pool together funds to acquire rare NFTs. However, it focuses only on Nouns, a generative art NFT project. So far, SharkDAO has acquired 5 nouns and has 400 members (or as they call it, ‘Sharks’), together raising 1000 ETH. Here, members will receive SHARK tokens in exchange for ETH. Then, with this token, members can vote and “steer the mission” and how they “deploy resources”.

Jenny Metaverse DAO
Jenny Metaverse DAO, set up on the Unicly platform, acquires NFTs and stores them in a vault. Additionally, the native uJENNY token represents the NFTs. As with WHALE, those who hold the token holders get governance rights and can vote on decisions such as releasing NFTs from the vault, acquiring NFTs, and more.
How to Create a DAO
If you want to create a DAO of your own, easiest way is through an open-source platform. There are lots to choose from and most of them are no-code solutions. Apart from that, you’ll need to do the following:
- Define the purpose/structure of the DAO
- Establish the DAO tokens and their uses
- Set up a voting mechanism
- Establish a treasury
- Build a community
Of course, there’s actually way more to it than that. If you want a step by step process, check out our full guide on how to create a DAO.
The future of decentralized organizations
Clearly, DAOs have a number of use-cases within the NFT industry. In the coming months and years, these use cases are only going to grow. Moreover, their vision of an organization owned and managed by its members could one day even replace some traditional organizations. In the future, Decentralized Autonomous Organizations could also become a must-have for NFT projects. Meaning, we will likely see a flurry of DAO activity in the next year and further.
All investment/financial opinions expressed by NFTevening.com are not recommendations.
This article is educational material.
As always, make your own research prior to making any kind of investment.








